What is a private cloud? What are the advantages of private cloud in a multicloud environment
Published February 28, 2024. 1 min readWhat is a private cloud?
A private cloud refers to a cloud computing environment that is dedicated solely to one organization, whether it be a business, government agency, or other entity. Unlike public clouds, which are shared by multiple organizations, a private cloud is designed to provide exclusive access and control over computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking infrastructure.

Key characteristics of a private cloud
- Dedicated infrastructure: Private clouds typically utilize dedicated hardware resources, either on-premises within an organization's data center or hosted by a third-party provider. This ensures that the computing environment is isolated and solely dedicated to the organization's use.
- Enhanced security and compliance: Private clouds offer greater control and security over data and applications compared to public clouds. Organizations can implement stringent security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and network segmentation, to safeguard sensitive information and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
- Customization and flexibility: Private clouds allow organizations to customize the infrastructure and configuration according to their specific requirements and workload demands. This flexibility enables greater performance optimization and resource allocation tailored to the organization's needs.
- Scalability and resource pooling: Despite being dedicated, private clouds still offer scalability and resource pooling capabilities similar to public clouds. Organizations can dynamically allocate computing resources to different workloads based on demand, thereby optimizing resource utilization and scalability.
- Cost control: While private clouds may require upfront investment in infrastructure and maintenance, they offer predictable costs and greater control over expenditure compared to public clouds, where pricing is often based on usage and consumption.
Private cloud examples and use cases
Once an organization has assessed its cloud requirements and priorities, it can determine whether a private cloud computing environment is the most suitable IT solution.1. Ensuring HIPAA Compliance For certain organizations, particularly those operating in industries with stringent regulatory requirements, a private cloud may be the most practical option to maintain compliance. Consider a financial institution subject to regulations like the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), which mandates strict measures for protecting sensitive financial data. Compliance with PCI DSS requires robust security protocols to safeguard customer information and prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.In this context, XYZ Hosting Solutions stands out as a certified provider, ensuring that its private cloud environment aligns with the standards outlined in PCI DSS regulations. Additionally, integrating security services like XYZ Security Suite with the private cloud infrastructure enhances data protection and meets compliance requirements effectively.2. Flexibility requirements Organizations seeking increased flexibility in their IT infrastructure can benefit significantly from deploying a private cloud environment. This is particularly relevant for medium to large businesses running diverse applications, each with its unique resource demands.By virtualizing servers hosting various applications, organizations can dynamically allocate resources based on workload requirements. For example, allocating additional computing power or memory to servers running resource-intensive applications like email enhances performance without incurring additional hardware costs. This approach optimizes resource utilization, resulting in cost savings and improved scalability.
Key considerations for cloud deployment
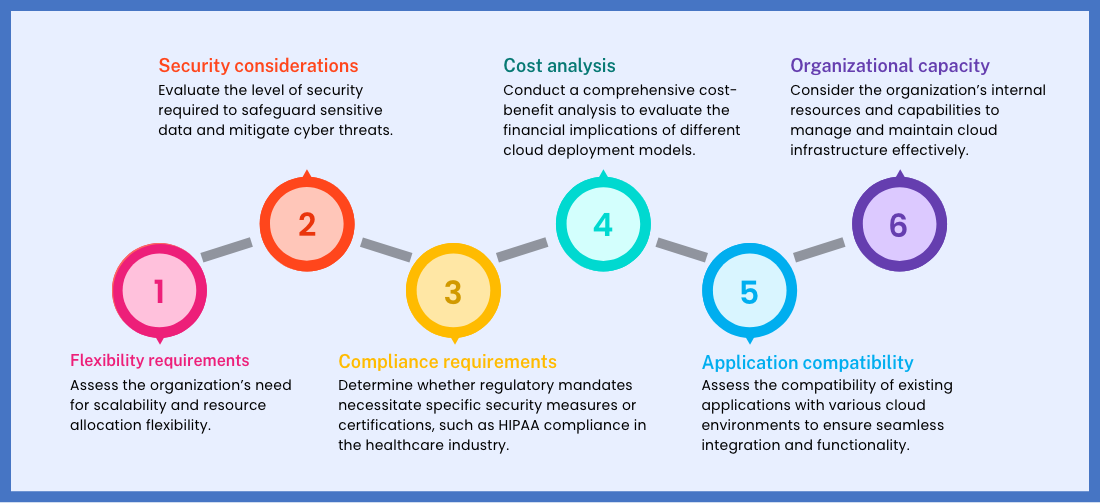
When evaluating cloud deployment options, organizations should consider several factors to ensure alignment with their operational needs and objectives:
Engaging with a trusted cloud service provider
Partnering with a reputable cloud service provider specializing in hosted private cloud solutions can streamline the cloud adoption process and provide tailored recommendations based on the organization's unique requirements. These providers offer expertise in evaluating cloud needs, implementing robust security measures, and optimizing cloud infrastructure for performance and efficiency.
Private cloud in a multicloud environment
In today's fast-paced digital era, organizations are constantly seeking innovative ways to leverage cloud technologies to drive business growth and gain a competitive edge. A widely acknowledged trend in cloud adoption is the move towards multicloud environments, where enterprises utilize multiple hyperscale public clouds alongside private cloud solutions. While the benefits of multicloud are well-documented, the pivotal role of private cloud solutions is often overlooked. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the rationale behind incorporating private cloud into multicloud strategies, highlighting its advantages, real-world applications, and the imperative need for expert partners like Rackspace Technology to navigate this complex terrain effectively.
Understanding the multicloud imperative
Multicloud adoption has gained significant traction in recent years, driven by various factors such as risk diversification, avoidance of vendor lock-in, and the ability to harness the best cloud capabilities across different providers. However, amidst the fervor for public cloud services, the importance of private cloud solutions cannot be overstated. Private cloud environments offer distinct advantages, particularly for workloads that cannot fully exploit the features of public clouds. Real-life examples abound, illustrating scenarios where certain applications or sensitive data necessitate the enhanced control and security afforded by private cloud deployments.
Considerations for private cloud integration
When formulating a multicloud strategy, organizations must carefully weigh the benefits of incorporating private cloud solutions. Compliance requirements, data sovereignty concerns, and the potential impact of data transfer fees all underscore the need for a dedicated private cloud option. For instance, industries subject to stringent regulatory frameworks, such as healthcare or finance, may find that hosting sensitive data in a private cloud provides greater assurance and compliance adherence compared to public cloud alternatives. Additionally, by prioritizing a private cloud as the primary data repository within a multicloud environment, organizations can mitigate data transfer costs and optimize operational efficiency.
Advantages of hosted private cloud solutions
The adoption of a hosted private cloud as part of a multicloud strategy offers remarkable advantages:
- Transition away from on-premises data centers: Hosted private clouds enable organizations to eliminate the need for on-premises data centers, reducing operational overhead and freeing up resources.
- Seamless integration of legacy workloads: Private clouds effortlessly accommodate legacy workloads, providing a smooth transition path for organizations with existing infrastructure.
- Provisioning of customized infrastructure: Private clouds allow for the provisioning of tailor-made infrastructure to meet the specific requirements of specialized workloads, enhancing performance and efficiency.
- Reduction in real estate costs: By leveraging hosted private clouds, organizations can typically reduce real estate expenses associated with maintaining physical data center facilities.
- Simplified data sovereignty and compliance: Dedicated private clouds offer a straightforward approach to data sovereignty and compliance, ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements and mitigating associated risks.
- Minimization of data transfer charges: Making a private cloud the primary data store in a multicloud environment can help minimize data transfer charges, resulting in cost savings.
- Elimination of performance impacts from noisy neighbors: With dedicated private clouds, organizations avoid the performance impacts caused by shared resources and noisy neighbors commonly encountered in public cloud environments.
Navigating legacy systems and compliance challenges
One of the key challenges in modernizing IT operations lies in balancing the need to adapt to new technologies while preserving operational resilience and cost-effectiveness. Legacy systems, often entrenched in business-critical operations, pose a significant hurdle to cloud migration efforts. For instance, bespoke enterprise applications like ERP or CRM systems may require extensive refactoring to transition to the public cloud, rendering such endeavors economically unfeasible for many organizations. In such scenarios, managed hosted private cloud solutions emerge as a viable compromise, allowing businesses to reduce expenses and mitigate risk while maintaining compatibility with legacy systems.
Real-world applications and success stories
Numerous industries have successfully leveraged hosted private cloud solutions to address specific business challenges and regulatory requirements. For example, a leading healthcare provider opted for a managed private cloud to ensure HIPAA compliance and safeguard patient data, while a financial services firm utilized hosted private cloud infrastructure to support its mission-critical trading applications with stringent performance and security requirements. These real-world examples underscore the versatility and efficacy of private cloud solutions in diverse business contexts.
Best practices for successful cloud implementation
Transitioning to a cloud-based infrastructure requires careful planning and execution. To ensure a smooth and successful migration process, organizations should adhere to the following best practices:
- Allocate a dedicated budget for the cloud migration project and regularly review and adjust it as needed.
- Establish protocols for employee training and access control to ensure proper utilization and security of cloud resources.
- Implement robust data encryption, backup, and recovery protocols to safeguard against data loss or breaches.
- Enforce unified security standards across the organization to mitigate cyber threats and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Organize and optimize file storage systems before migrating to the cloud to streamline data management and access.
- By following these best practices and leveraging the expertise of trusted cloud service providers, organizations can maximize the benefits of private cloud solutions while effectively addressing their IT needs and objectives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of private cloud solutions within multicloud environments presents significant advantages and opportunities for organizations navigating the complexities of modern IT landscapes. Private clouds offer unparalleled control, security, and customization, making them an ideal choice for industries with stringent regulatory requirements, legacy workloads, or specialized infrastructure needs. By leveraging hosted private cloud solutions, organizations can transition away from on-premises data centers, streamline compliance efforts, and optimize operational efficiency while minimizing costs. Real-world examples underscore the versatility and efficacy of private cloud deployments across diverse business contexts, from healthcare to finance. Moreover, adhering to best practices for cloud implementation ensures a smooth migration process and maximizes the benefits of private cloud solutions. In an era marked by rapid technological advancements and evolving business demands, the strategic adoption of private cloud within a multicloud strategy, supported by expert partners positions organizations for success in driving innovation, agility, and growth.CTA: Know more about our cloud enablement services here: (https://www.enlume.com/services/cloud-enablement/)
IN THIS ARTICLE
- What is a private cloud?
- Key characteristics of a private cloud
- Private cloud examples and use cases
- Key considerations for cloud deployment
- Engaging with a trusted cloud service provider
- Private cloud in a multicloud environment
- Understanding the multicloud imperative
- Considerations for private cloud integration
- Advantages of hosted private cloud solutions
- Navigating legacy systems and compliance challenges
- Real-world applications and success stories
- Best practices for successful cloud implementation
- Conclusion
.png)